Centrifugal pumps and magnetic drive pumps are widely used in daily industrial production, especially in the fields of chemical, pharmaceutical and environmental protection. These two chemical pumps have their own advantages in practical applications.
Although traditional centrifugal pumps are widely used, their leakage risks and maintenance difficulties have always been the pain points of the industry. In contrast, magnetic drive pumps have become the first choice for dangerous fluid transportation with their "zero leakage" characteristics.
This article deeply explores the difference between magnetic drive pumps and centrifugal pumps, and provides enterprises with a scientific basis for equipment selection.
The difference between magnetic drive pumps and centrifugal pumps 1: working principle
1. Magnetic drive pump: magnetic field non-contact seal
The zero leakage principle of magnetic drive pumps is derived from its innovative magnetic coupling transmission technology. Power is indirectly transmitted from the motor to the impeller through the magnetic interaction between the inner and outer magnetic rotors, without the need for physical shaft connection.
This design completely abandons the traditional mechanical seal, completely encloses the medium in a stationary sealing shell, and achieves "zero leakage". The magnetic drive efficiency of magnetic drive pumps exceeds 95%, which is an ideal choice for conveying hazardous media such as hydrofluoric acid and liquid chlorine.
2. Centrifugal pump: mechanical drive by centrifugal force

Centrifugal pumps rely on the centrifugal force generated by the high-speed rotation of the impeller to push the fluid. The motor directly drives the impeller shaft through the coupling, and the dynamic mechanical seal (such as packing seal or mechanical seal) is the key anti-leakage component.
However, the defects of the mechanical seal of the centrifugal pump are quite obvious - about 30% of centrifugal pump failures are caused by seal failure, especially under high temperature and high pressure conditions.
The difference between magnetic drive pumps and centrifugal pumps 2: structural design
1. Magnetic drive pump structure
The magnetic drive pump consists of three parts: pump body, magnetic drive assembly and motor. The magnetic drive assembly includes an outer/inner magnetic rotor and a non-magnetic sealing shell.
When the motor drives the outer rotor, the inner rotor (connected to the impeller) rotates synchronously to achieve non-contact power transmission. The sealing shell is made of corrosion-resistant materials such as Hastelloy or ceramics, which acts as a static seal to isolate the rotor and prevent medium leakage.
2. Centrifugal pump structure
The centrifugal pump consists of an impeller, a pump body, a shaft, a bearing and a mechanical seal. Its dynamic sealing parts (such as mechanical seal rings) are prone to wear and corrosion, which can lead to leakage.
The annual maintenance cost of centrifugal pumps is 40% higher than that of magnetic pumps, mainly due to seal replacement and leak repair.
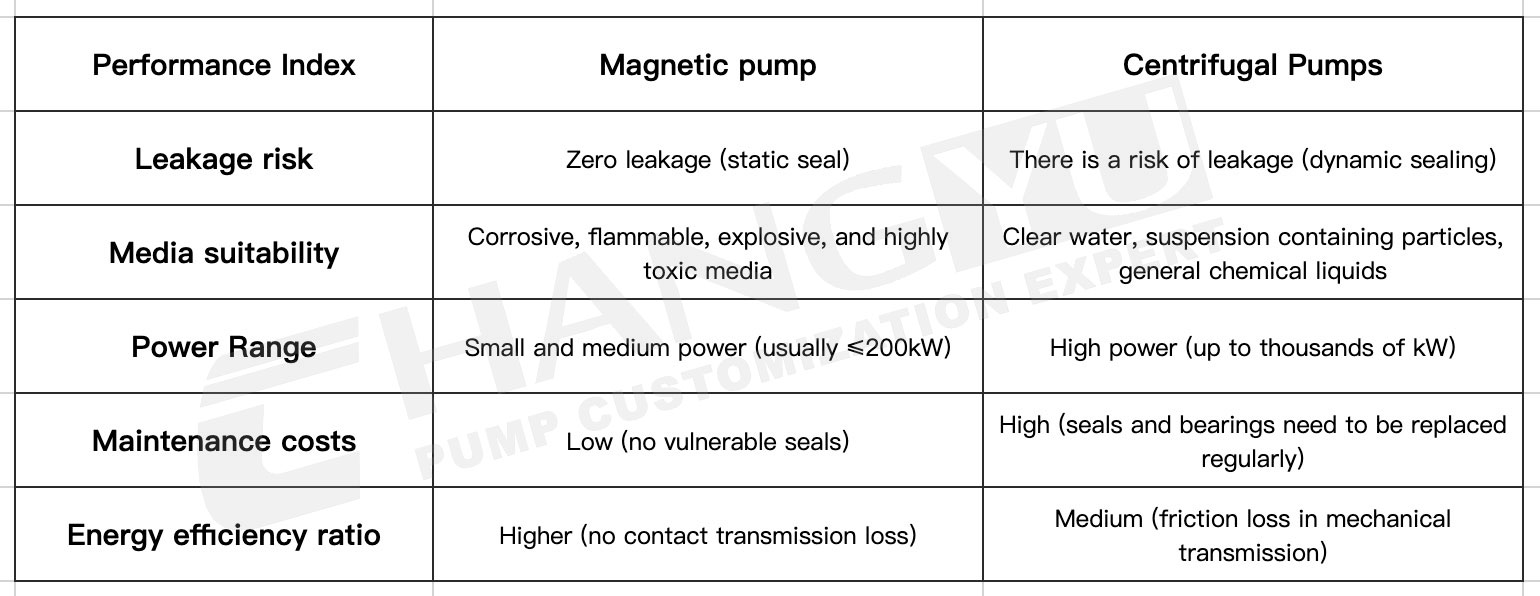
The difference between magnetic drive pumps and centrifugal pumps 3: performance parameters
The difference between magnetic drive pumps and centrifugal pumps 4: industry applications
1. Application of magnetic pumps
The zero leakage advantage makes magnetic pumps an ideal choice for flammable, explosive, highly corrosive or toxic media:
Chemical industry: conveying sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid, etc. (in accordance with ASME B73.3 standards).
Pharmaceutical industry: conveying high-purity fluids in a sterile environment to prevent contamination.
Nuclear energy: sealed conveying of radioactive media to ensure operator safety.
2. Application of centrifugal pumps
Centrifugal pumps excel in cost-sensitive and efficient applications:
Municipal water supply: high-flow, cost-effective clean water delivery.
Sewage treatment: handling sludge containing solid particles, wear-resistant.
Agricultural irrigation: conveying low-viscosity fluids over long distances in various environments.

There are significant differences between magnetic drive pumps and centrifugal pumps, each with its own unique advantages. By gaining a deeper understanding of these differences, companies can achieve optimal safety and cost-effectiveness in chemical pump selection, thereby promoting sustainable operational practices.



















